Last Updated on: 6th November 2023, 01:10 pm
Web site: www.86dos.org (not active)
Origin: USA
Category: Workstation
Desktop environment: CLI
Architecture: x86
Based on/Family: DOS
Wikipedia: 86-DOS
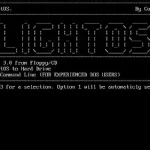
Media: Install Floppy Disk
The last version | Released: 1.10 | July 1981
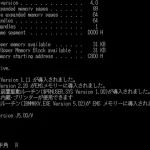
86-DOS (QDOS for Quick and Dirty Operating System) – an operating system developed by Seattle Computer Products for its Intel 8086-based computer kit.
86-DOS provides the tools needed to develop programs for the 8086, as well as a hardware-independent environment in which to run these programs. It is a very modular system. At its core is the disk file manager and I/O device handler, and everything else is considered a “user program”. This allows the system to be easily tailored to any custom requirements.
The disk file manager allows programs to create and access disk files by name. Files may be read or written sequentially or randomly, and number of records at a time.
A program called COMMAND provides the interface between the user at the console and the file manager. COMMAND allows the users to display the disk directory, rename, destroy, or copy files, and execute other programs, such as the assembler, editor, or source code translator.
The assembler reads a source files of Intel-like 8086 mnemonics from disk, and produces a listing file and an Intel hex format object file.
The editor is line oriented, suitable for creating and maintaining program files.
The source code translator can translate most Z80 source code into 8086 source code acceptable to the assembler after minor manual correction. This provides a relatively quick and easy way to transport programs between the processors.
86-DOS is not related to the CP/M operating system of Digital Research. Disk directory formatting and space allocation are completely different and incompatible. 86-DOS does, however, provide a utility called RDCPM which will transfer files from CP/M disks to 86-DOS disks. Further, operating system calls and calling conventions have been provided which make possible automatic translation of Z80 programs written for CP/M into 86-DOS programs that run under 86-DOS.
86-DOS boots and runs on the SIMH/AltairZ80 Simulator. The latest version (based on SIMH 3.8-0) is available from Peter Schorn’s website.